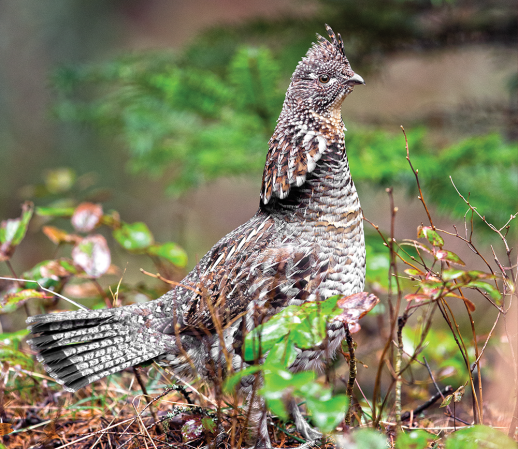
Hit the ground and start walking. That’s the strategy most hunters employ when they enter the woods in search of ruffed grouse. “Cover enough country and sooner or later I’ll find them,” they say to themselves. Add a few weeks of hunting pressure and waning food to the equation, and it all gets a bit tougher.
But you can save steps, increase your flush count, get more shots, and bag more birds if you use some common sense and follow the program below. Ruffed grouse utilize different parts of their habitat at different times of day. Here’s where to hunt and when.
Early Morning: Timber Seams
Don’t believe sleepyhead late-risers who rationalize that grouse hunting is better at midmorning. Hit the woods at sunrise, when the birds have just flown down and are moving out and laying down some scent for your dog. Even if you hunt without a canine, grouse are on the move and more vulnerable now.
Hunt seams and transitions between big, mature timber (where birds like to roost), open areas, and the thick brush where grouse spend the bulk of their day. Another good zone is the seam between conifers, such as pines or spruce, and hardwoods.
Midmorning: Feeding Zones
By the time the sun has been up for an hour, most grouse have arrived at their feeding area and are foraging hard. Know what the birds are eating: If you shoot a grouse, open up its crop and check inside. Then hunt that kind of feed.
Gray dogwood thickets are great. Grouse love the green-gray berries, as well as red snowberries and highbush cranberries, plus most any other juicy or freeze-dried fruit, such as crab apples. Abandoned orchards are grouse heaven. If there are oaks around, grouse will look for small acorns and pieces. Work the edges of open areas like hay meadows and abandoned fields, where grouse will hunt insects and pick up seeds. Logging roads and tote trails with clover are also prime.
Afternoon: Thick Stuff
After feeding, ruffs work their way into the thick stuff, where they will loaf and spend the day under cover. As a general rule, think “low” and/or “damp” now–along brooks, creeks, marshes, bogs, and seeps.
Head for stands of young aspen–trunks from buggy-whip-thick to fencepost diameter are about right. Grouse love tag alder thickets, especially where that cover butts up to timber or wetlands. Brushy tangles of witch hazel, raspberry canes, and multiflora rose hold birds. So do deadfalls. On windy days, kick around in the grassy edges of some of the thickest cover.
Late Afternoon: Feeding/Gritting Areas
By late afternoon, grouse are out feeding again, as well as pecking for grit.
Hit the kinds of feeding areas discussed above. Also work sandy lanes, dirt roads, and the edges of other open areas where birds pick up grit.
Evening: Transition Corridors
You can hunt grouse right up to sunset, and this is a great time to be out, when the birds are back on the move toward roosting areas. Research indicates that grouse prefer to roost in and under deciduous and evergreen trees and shrubs, in brush piles, and in leaf litter. When cold weather hits, grouse will snow roost unless conditions are unsuitable. Conifers are then the roost cover of choice. Try hunting the transitions between stands of young timber and thick brush, or young timber and mature trees. If the evening is windy, stick to lower ground where birds find protection and quiet.